How else do we learn about our creek beds and their healthy or climate than taking a look at them up close and personally? I ventured into our creek beds which gave me an awesome understanding of our fair Evergreen. Today, we’re going to discuss a creek bed which is the namesake for the Western region of Evergreen between its namesake and Coyote Creek.
How else do we learn about our creek beds and their healthy or climate than taking a look at them up close and personally? I ventured into our creek beds which gave me an awesome understanding of our fair Evergreen. Today, we’re going to discuss a creek bed which is the namesake for the Western region of Evergreen between its namesake and Coyote Creek.
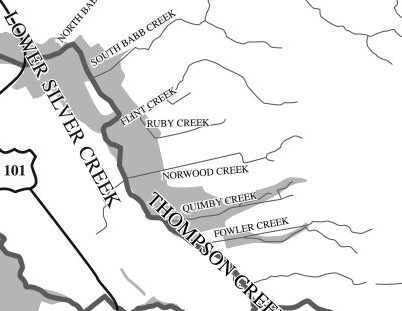
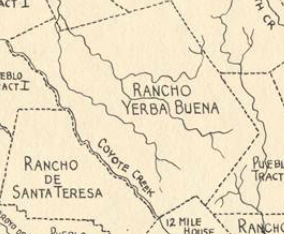
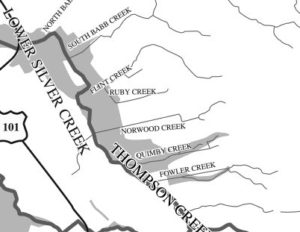 That’s right. I’m talking about Silver Creek. I went to Silver Creek High School, built in 1969, and never once wondered why the name. When I first started this project, it appeared that Silver Creek was an important part of Evergreen’s story. Farmers with land attached to creeks had the upper hand. Before Silver Creek, the area, was an idea, the creek was there and Cunningham Lake was named Silver Lake. This creek must’ve been so large, it contributed to the naming of the region. In fact, the whole network of creeks through Evergreen contribute to the Lower Silver Creek Watershed.
That’s right. I’m talking about Silver Creek. I went to Silver Creek High School, built in 1969, and never once wondered why the name. When I first started this project, it appeared that Silver Creek was an important part of Evergreen’s story. Farmers with land attached to creeks had the upper hand. Before Silver Creek, the area, was an idea, the creek was there and Cunningham Lake was named Silver Lake. This creek must’ve been so large, it contributed to the naming of the region. In fact, the whole network of creeks through Evergreen contribute to the Lower Silver Creek Watershed.
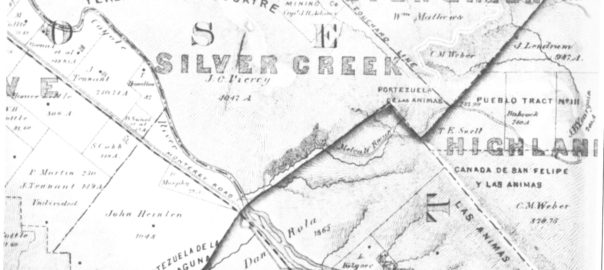
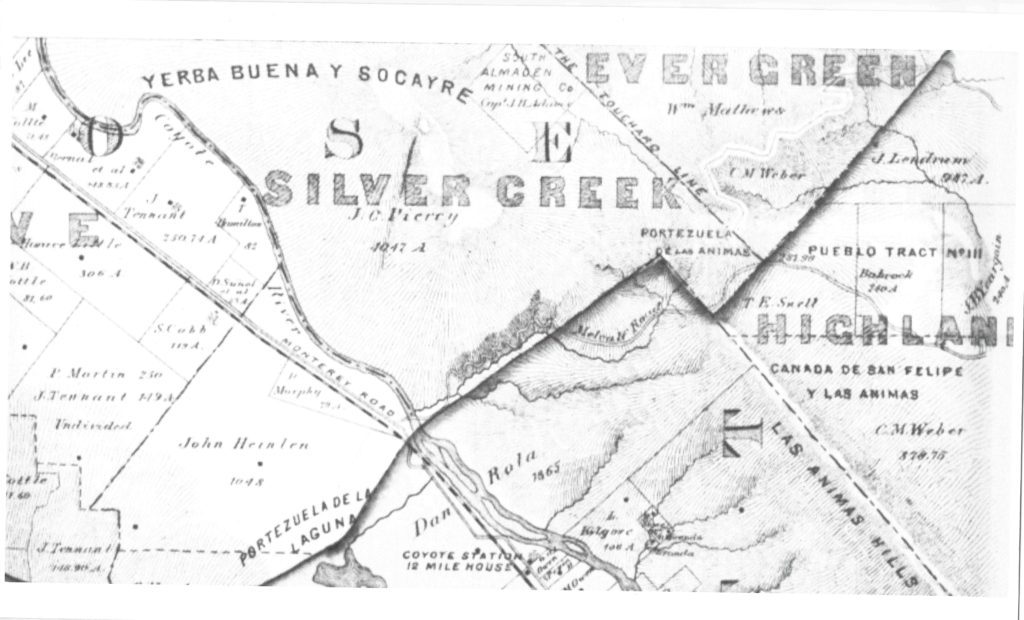
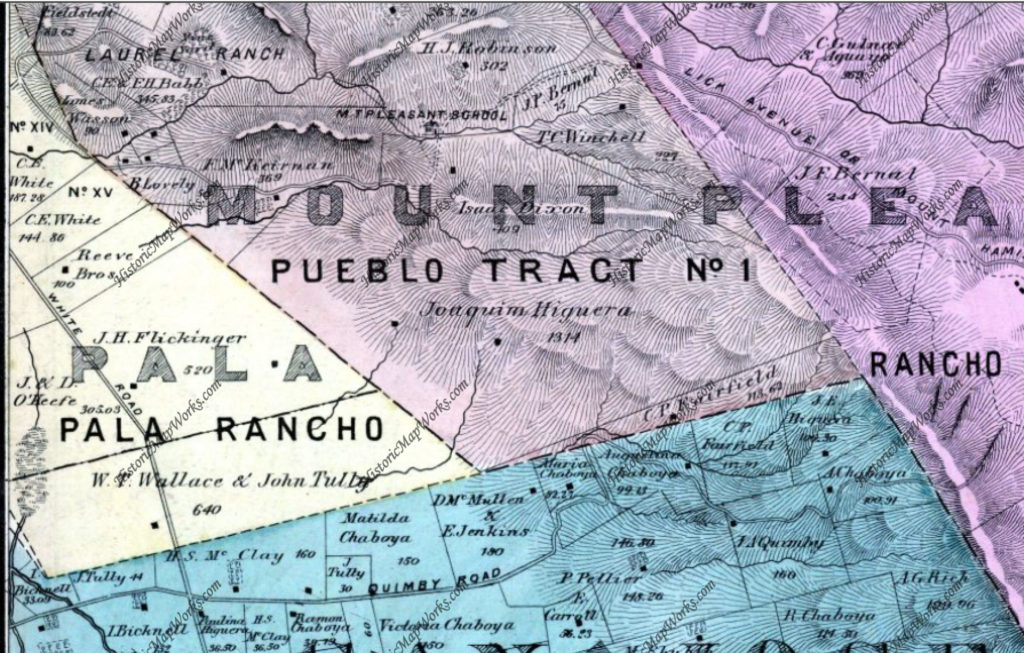
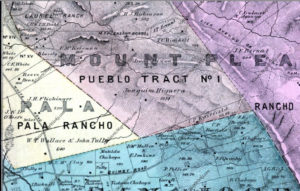
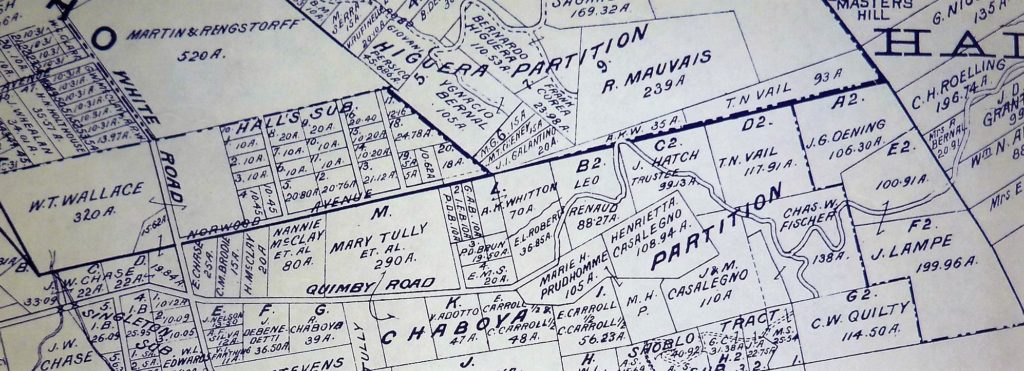
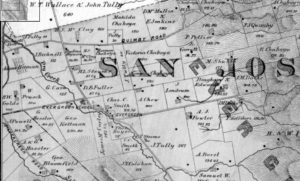
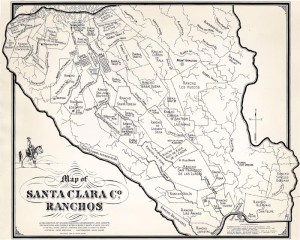
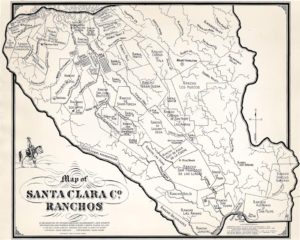
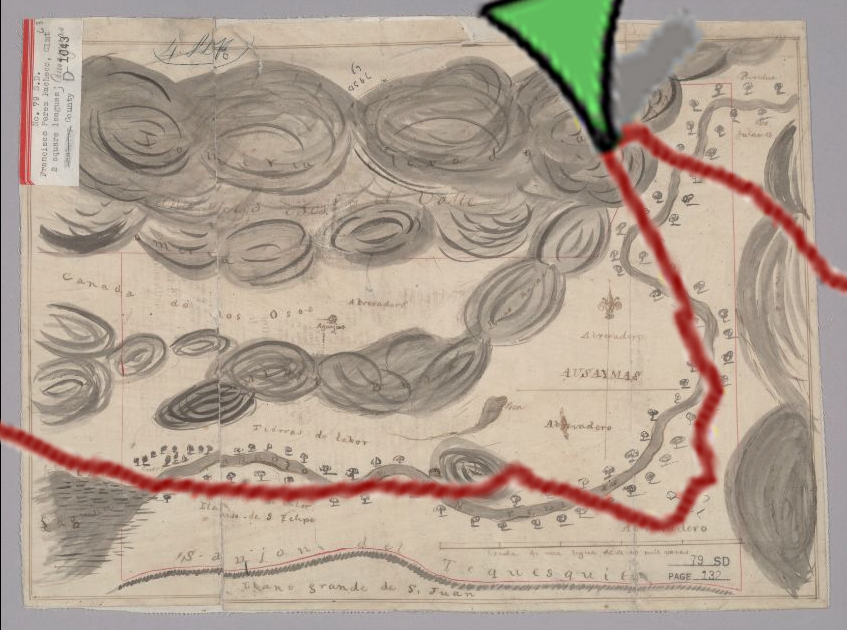
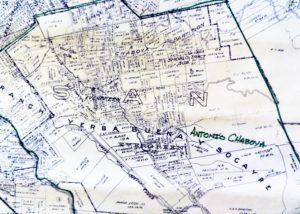
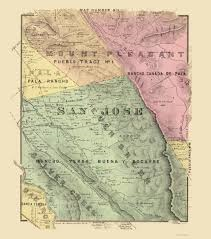 Silver Creek, as in the neighborhood and Evergreen’s first high school, has beenlocated on maps at least into the 1860’s. Silver Creek, the area and the Creek, are historic. This 1867 Altas shows it off predominantly. It’s 2 miles outside of Downtown Evergreen, located off San Felipe Road and Evergreen Road. It might’ve grown up as a town had stores not opened in nearby Township of Evergreen. Because of its closeness to Edenvale and Downtown San Jose, it was incorporated into the City Limits earlier than Downtown Evergreen. Evergreen is the entire Rancho Yerba Buena. This area too being so far West would’ve been settled pretty early on by squatters. Some of the defendants in the Chaboya case from these area specifically were the Cottle Family.
Silver Creek, as in the neighborhood and Evergreen’s first high school, has beenlocated on maps at least into the 1860’s. Silver Creek, the area and the Creek, are historic. This 1867 Altas shows it off predominantly. It’s 2 miles outside of Downtown Evergreen, located off San Felipe Road and Evergreen Road. It might’ve grown up as a town had stores not opened in nearby Township of Evergreen. Because of its closeness to Edenvale and Downtown San Jose, it was incorporated into the City Limits earlier than Downtown Evergreen. Evergreen is the entire Rancho Yerba Buena. This area too being so far West would’ve been settled pretty early on by squatters. Some of the defendants in the Chaboya case from these area specifically were the Cottle Family.
 Evergreen was a haven for farmers because of its creeks and natural water delivery system in gravity, hillsides and natural springs throughout Evergreen. Springs will appear whenever seismic activity is taking place, like Silver Creek and the Silver Creek Mines behind Silver Creek Valley Country Club. Oak Trees and wild berries line the creek bed, with poppies, wild lupin and grasses around the surrounding hills. These Oaks are Coastal Live Oak for the most part, even though Evergreen hosts a wide variety of oak trees. An illness makes oak trees white like this. It’s called root canker. Amongst the spectrum of oak diseases, Silver Creek’s oaks are really looking pretty good.
Evergreen was a haven for farmers because of its creeks and natural water delivery system in gravity, hillsides and natural springs throughout Evergreen. Springs will appear whenever seismic activity is taking place, like Silver Creek and the Silver Creek Mines behind Silver Creek Valley Country Club. Oak Trees and wild berries line the creek bed, with poppies, wild lupin and grasses around the surrounding hills. These Oaks are Coastal Live Oak for the most part, even though Evergreen hosts a wide variety of oak trees. An illness makes oak trees white like this. It’s called root canker. Amongst the spectrum of oak diseases, Silver Creek’s oaks are really looking pretty good.
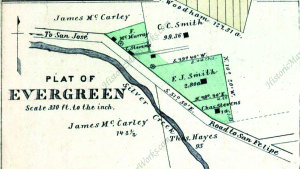
 Silver Creek’s ecosystem is fairly healthy, as indigenous birds and wildlife still call it home. Silver Creek’s existing water formations are very clean and free from pollutants. When I examine this Creek, the only littering I see is on road ways nearby – not in the water itself. Here, by Silver Creek Linear Park where Silver Creek appears to end, the Cottle’s cobble stone walls along the Dove Hill border are still evident.
Silver Creek’s ecosystem is fairly healthy, as indigenous birds and wildlife still call it home. Silver Creek’s existing water formations are very clean and free from pollutants. When I examine this Creek, the only littering I see is on road ways nearby – not in the water itself. Here, by Silver Creek Linear Park where Silver Creek appears to end, the Cottle’s cobble stone walls along the Dove Hill border are still evident.
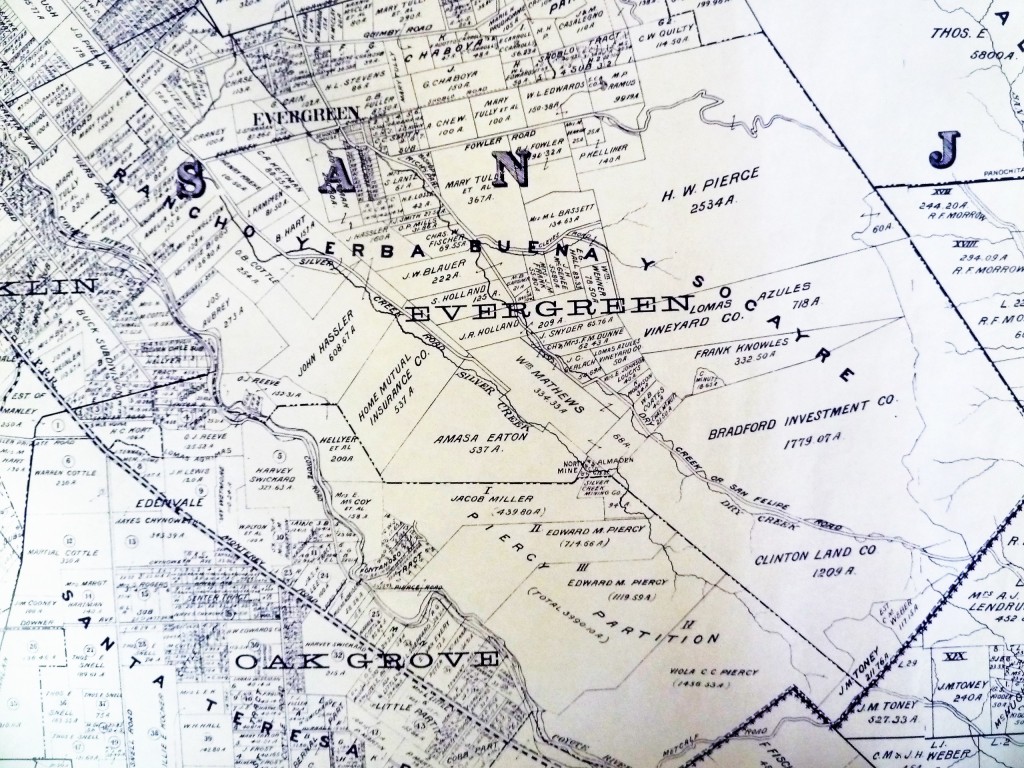
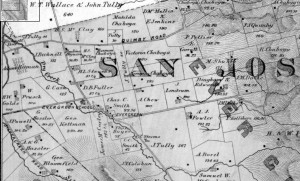
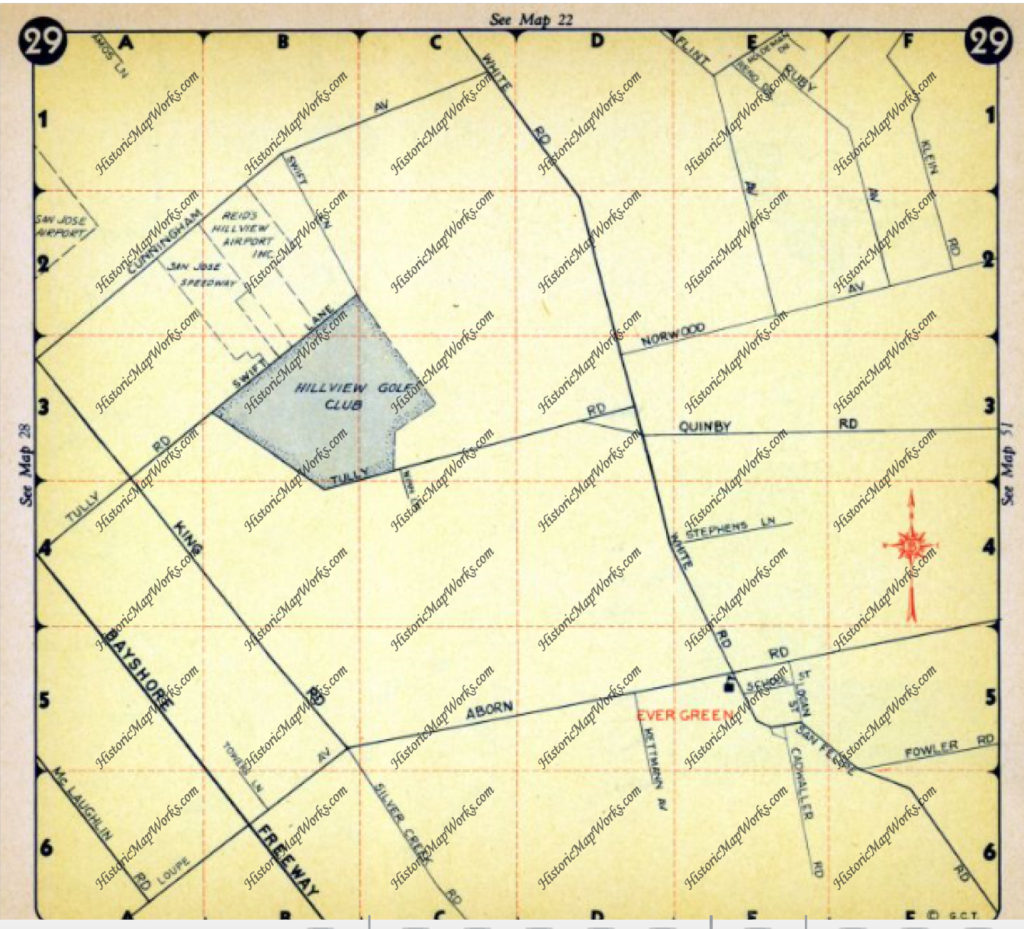
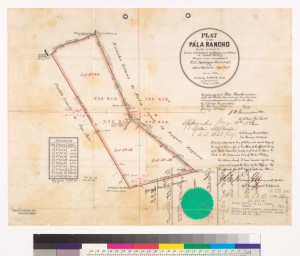
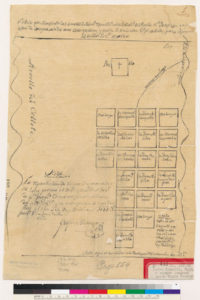
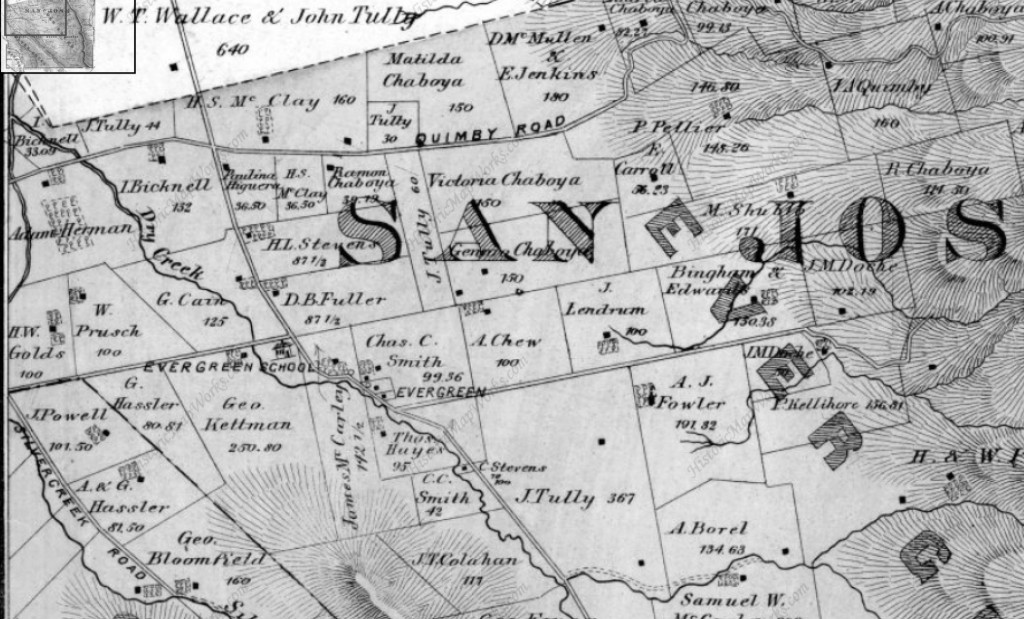
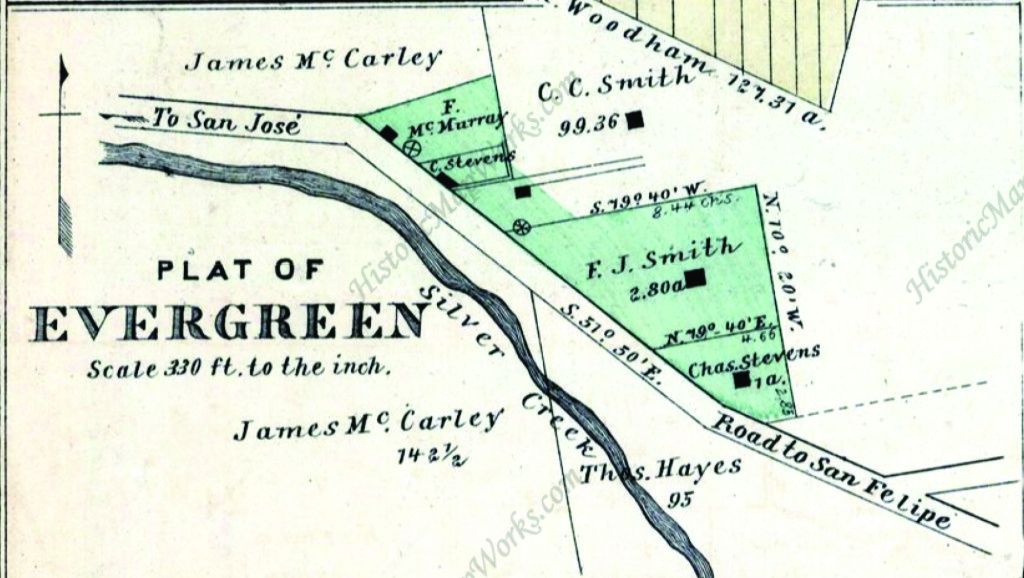
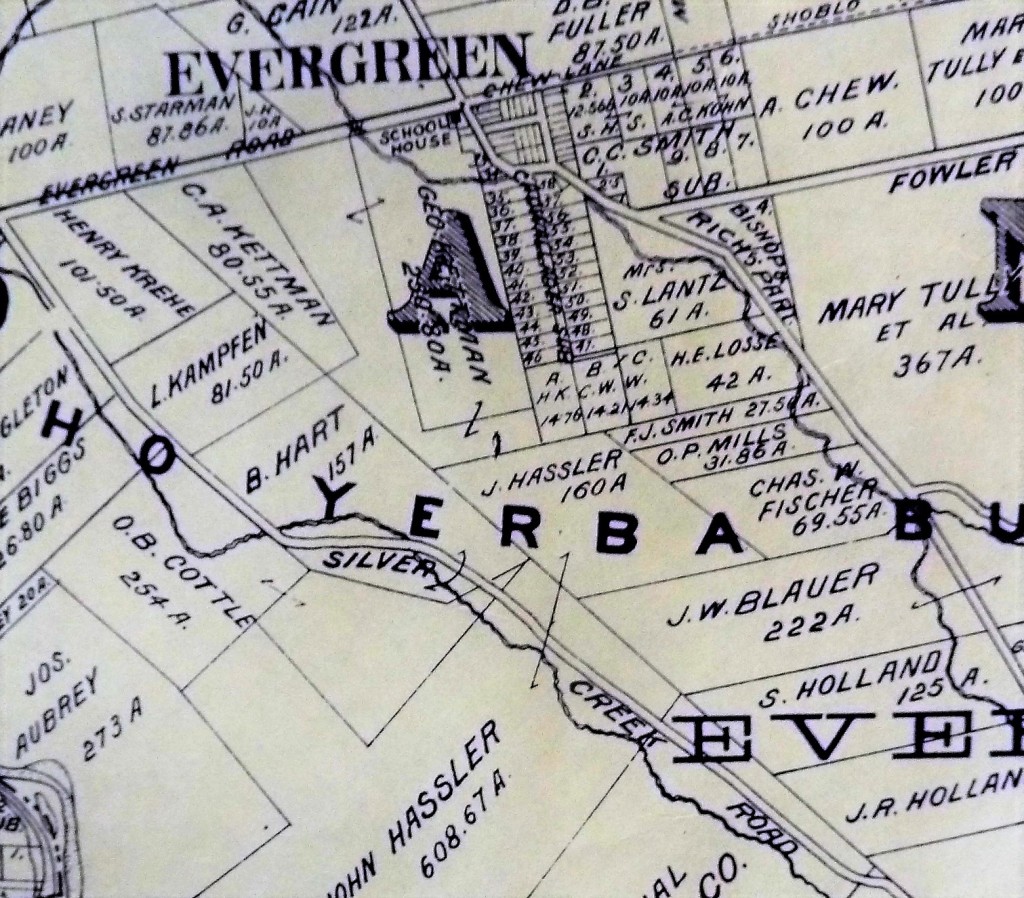
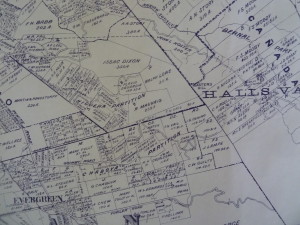
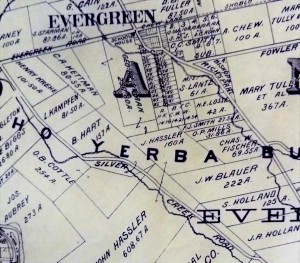 Silver Creek Road, King Road, White Road, Quimby Road and Evergreen Road back in those days were the huge arteries into Evergreen. You can see in this enlargement to the left that Silver Creek Road and the Creek intertwined through modern day “the Ranch” development over Hassler Parkway. Below you can view the entire length of the creek and roads. Where Silver Creek Road straightens out has always transitioned to King Road. King Road would’ve been the way to get to Downtown. Kinda still is.
Silver Creek Road, King Road, White Road, Quimby Road and Evergreen Road back in those days were the huge arteries into Evergreen. You can see in this enlargement to the left that Silver Creek Road and the Creek intertwined through modern day “the Ranch” development over Hassler Parkway. Below you can view the entire length of the creek and roads. Where Silver Creek Road straightens out has always transitioned to King Road. King Road would’ve been the way to get to Downtown. Kinda still is.
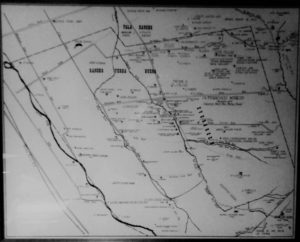 Silver Creek had its own grammar school at one point too. I couldn’t find it on an atlas map, but Evergreen historian and trusted source, Colleen Cortese, has it closer to Coyote Creek than Silver Creek, but hey. It served this whole area.
Silver Creek had its own grammar school at one point too. I couldn’t find it on an atlas map, but Evergreen historian and trusted source, Colleen Cortese, has it closer to Coyote Creek than Silver Creek, but hey. It served this whole area.
Silver Creek Road picks up again today near a Spring that contributes to Silver Creek’s Watershed. Springs are created by the geology in the surrounding areas, not the gathering of water heading down the slope like lots of Evergreen’s creeks.


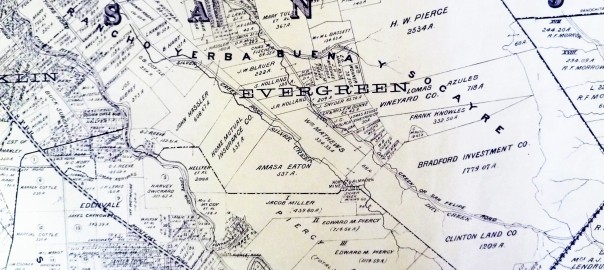
Silver Creek Mines are also located off of this portion of Silver Creek Road. You can see North Almaden Mines here in this 1890 map above. This same road used to connect over the hillside before its development. Bradford Investment was involved with the Mining Industry in those days, establishing Silver Creek Mines, and would’ve built this road through to his jobsite. You can see the entrance off San Felipe Road. The Hellyers and Piercys too would’ve mined in Silver Creek region. Brothers George and Daniel would choose opposite sides of Coyote Creek along the border with Edenvale, another small township. Coyote Creek creates the western most point of Silver Creek and therefore Evergreen. There’s a wicked rumor that someone accidently contaminated the Creek with quicksilver and their orchard turned to silver. This may or may not have happen to oak trees in the area.
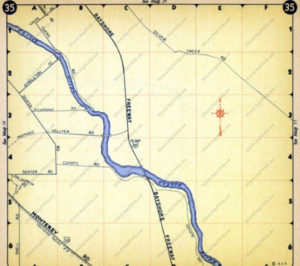 Until Silver Creek High School opened, students had to travel outside of Evergreen to go to school. The Creek would’ve existed where 101 lies now near the school. Many sections of Silver Creek, the Creek and the Road, have been paved over for the 101 Freeway in the 1930-40’s and built on top of for Silver Creek Valley Country Club’s construction in the 1990’s. Silver Creek Road which once followed the creek’s path also met up with San Felipe Road in the early 1900’s.
Until Silver Creek High School opened, students had to travel outside of Evergreen to go to school. The Creek would’ve existed where 101 lies now near the school. Many sections of Silver Creek, the Creek and the Road, have been paved over for the 101 Freeway in the 1930-40’s and built on top of for Silver Creek Valley Country Club’s construction in the 1990’s. Silver Creek Road which once followed the creek’s path also met up with San Felipe Road in the early 1900’s.
Silver Creek is a giant chunk of Evergreen, like a third. It’s presence influenced people to settle in and raise their farms and families here. Silver Creek is older than any Country Club, Park, or School. All this time, I thought it just described nearby Dry Creek / Thomspon Creek when this was the larger watershed hooked up to Silver Lake or now Cunningham. Here’s the Artwork featuring Silver Creek.