The town of 
 Evergreen, still not apart of San Jose, was known for many things at the turn of the 20th century. One of the things, besides its plentiful fruit and famed wines, that put the Village of Evergreen and City of San Jose on the national map was the invention of modern flight. The inventor, engineer, and dare-devil John J. Montgomery would flight Man’s first controlled flight in 1883 and take flights from the Evergreen hillsides and in downtown San Jose in the early 1900’s. Montgomery and fellow aviator, Daniel Maloney, would give their lives for their passion and invention of flight.
Evergreen, still not apart of San Jose, was known for many things at the turn of the 20th century. One of the things, besides its plentiful fruit and famed wines, that put the Village of Evergreen and City of San Jose on the national map was the invention of modern flight. The inventor, engineer, and dare-devil John J. Montgomery would flight Man’s first controlled flight in 1883 and take flights from the Evergreen hillsides and in downtown San Jose in the early 1900’s. Montgomery and fellow aviator, Daniel Maloney, would give their lives for their passion and invention of flight.
John J. Montgomery, the son of a prominent lawyer brought out West by the Gold Rush, was born in 1858 in Yuba City/Marysville. As a boy, John Montgomery would observe flight through birds in the sky and use that as inspiration throughout his work. Montgomery would also be inspired by another early aviator’s demonstration during his boyhood. The Montgomery family would move into Oakland in 1864, where his father held a successful law practice. In Millbrae in 1869, a young John Montgomery would witness the flight of an airship, closer to a zeppelin or blimp, called the Avitor Hermes, Jr. Young Montgomery would go home to Oakland and build a model for himself. Only a hand full of people had ever been in flight. Back then, ships would be lifted by balloons of helium or hydrogen, and were only in air for a very limited amount of flight time, a matter of seconds, before descent.
 People have been fascinated with flight but baffled by its execution. In a Greek Myth, Icarus would try to fly with wings of feathers and wax that melted as he approached the Sun. This creates the message that flight is beyond our grasp. There were totally kites going back in history. Leonardo Da Vinci would dream of inventing planes and helicopters in the 15th-16th century. Hot air balloons and the like would be used in the later half of the 18th century. Before John Montgomery’s time, balloons would be the only way to make flight possible, pioneered by Jacques Charles and the Robert brothers. The obstacle with preceding inventions for flight would fall short because they were too heavy to launch from the ground. The planes would simply fall.
People have been fascinated with flight but baffled by its execution. In a Greek Myth, Icarus would try to fly with wings of feathers and wax that melted as he approached the Sun. This creates the message that flight is beyond our grasp. There were totally kites going back in history. Leonardo Da Vinci would dream of inventing planes and helicopters in the 15th-16th century. Hot air balloons and the like would be used in the later half of the 18th century. Before John Montgomery’s time, balloons would be the only way to make flight possible, pioneered by Jacques Charles and the Robert brothers. The obstacle with preceding inventions for flight would fall short because they were too heavy to launch from the ground. The planes would simply fall.
 John Montgomery attended St. Ignatius College in San Francisco, graduating in 1879 and obtaining his Masters in 1880. James Lick Observatory would begin construction in 1879 and John would’ve become aware of Santa Clara County’s elevations. Montgomery would start designing his flying machines in San Diego County in 1881 when his family moved there after college. After his hours working on the farm, he would pour the left over energy into his theories. John Montgomery would build models in the barn’s attic. These first designs, Montgomery would work with a flapping wing like Leonardo Da Vinci’s sketch. The flapping wing wouldn’t be as effective as a fixed one.
John Montgomery attended St. Ignatius College in San Francisco, graduating in 1879 and obtaining his Masters in 1880. James Lick Observatory would begin construction in 1879 and John would’ve become aware of Santa Clara County’s elevations. Montgomery would start designing his flying machines in San Diego County in 1881 when his family moved there after college. After his hours working on the farm, he would pour the left over energy into his theories. John Montgomery would build models in the barn’s attic. These first designs, Montgomery would work with a flapping wing like Leonardo Da Vinci’s sketch. The flapping wing wouldn’t be as effective as a fixed one.
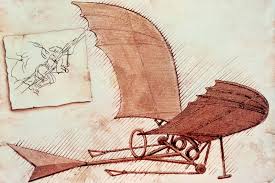
 In 1882-84, Montgomery would experiment with flight outside of San Diego along the Mexican border with “gliders”, a monoplane closer to a hang-glider than Leonardo’s flapping flying machine. Gliders would require perfect conditions to get and keep in flight or the aforementioned balloon would raise the machine hundreds of feet. This is a scene from Montgomery’s San Diego area workshop. This machine was inspired on the wings of seagulls. John J. Montgomery’s flights in the 1880’s would be the first heavier-than-air flight, the event observed by friends and family members but not widely publicized. This glider would’ve been a gull shaped, single winged flying machine, or a monoplane. The glider would ignore the “Yaw” or center of mass, the gravitational force towards that would swing from the heaviest point, the pilot. During this time, Octave Chanute, a contemporary critic, would have harsh words for Montgomery, but Montgomery’s pursuit of flight would continue.
In 1882-84, Montgomery would experiment with flight outside of San Diego along the Mexican border with “gliders”, a monoplane closer to a hang-glider than Leonardo’s flapping flying machine. Gliders would require perfect conditions to get and keep in flight or the aforementioned balloon would raise the machine hundreds of feet. This is a scene from Montgomery’s San Diego area workshop. This machine was inspired on the wings of seagulls. John J. Montgomery’s flights in the 1880’s would be the first heavier-than-air flight, the event observed by friends and family members but not widely publicized. This glider would’ve been a gull shaped, single winged flying machine, or a monoplane. The glider would ignore the “Yaw” or center of mass, the gravitational force towards that would swing from the heaviest point, the pilot. During this time, Octave Chanute, a contemporary critic, would have harsh words for Montgomery, but Montgomery’s pursuit of flight would continue.
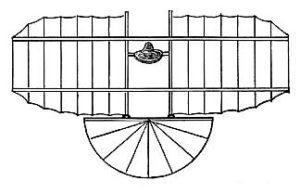 John J. Montgomery would continue experimenting and flying throughout California, in San Diego, San Francisco, Santa Cruz and Santa Clara Counties. To fund his inventions, John Montgomery would pursue other endeavors within physics and engineering. In 1884, Montgomery would be granted a patent for the process of vulcanizing and devulcanizing rubber.
John J. Montgomery would continue experimenting and flying throughout California, in San Diego, San Francisco, Santa Cruz and Santa Clara Counties. To fund his inventions, John Montgomery would pursue other endeavors within physics and engineering. In 1884, Montgomery would be granted a patent for the process of vulcanizing and devulcanizing rubber.
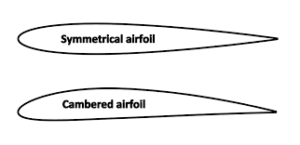 In 1885, Montgomery would start also experimenting with how air flowed over different shaped surfaces, adding considerably to the field of aerodynamics. Montgomery, still in San Diego County, would be so secretive about his experiments, no one knew what he was up to at the time but close family members. The fruit of this labor would later be written in trade publications and heard during groundbreaking Aviation Navigation discussions in the early 20th century. Inspired by the articulating wings of turkey vultures and eagles, he would being to tie the fixed wing to a guiding mechanism to keep the plane even or balanced. Montgomery’s research would prove a slightly curved surface best for his gliders. Montgomery would also start programming direction and counter-controls for gusts of wind and easy turning through a series of spring loaded mechanisms.
In 1885, Montgomery would start also experimenting with how air flowed over different shaped surfaces, adding considerably to the field of aerodynamics. Montgomery, still in San Diego County, would be so secretive about his experiments, no one knew what he was up to at the time but close family members. The fruit of this labor would later be written in trade publications and heard during groundbreaking Aviation Navigation discussions in the early 20th century. Inspired by the articulating wings of turkey vultures and eagles, he would being to tie the fixed wing to a guiding mechanism to keep the plane even or balanced. Montgomery’s research would prove a slightly curved surface best for his gliders. Montgomery would also start programming direction and counter-controls for gusts of wind and easy turning through a series of spring loaded mechanisms.
 John J. Montgomery was finally hearing through the newspapers and his brother, in New York, about other early aviators. This news and competition would inspire Montgomery to act upon his research, and be a part of the conversation in the new field of science.
John J. Montgomery was finally hearing through the newspapers and his brother, in New York, about other early aviators. This news and competition would inspire Montgomery to act upon his research, and be a part of the conversation in the new field of science.
In 1893, Montgomery attended the Chicago Columbian Exhibition to listen to Nikola Tesla speak about electricity. Once there, John would introduce himself to the aviation and physics professors, inventors and theorists. His networking paid off, and Montgomery would be invited to speak at the conference himself and gain through his experiments. Montgomery, gaining fame for his accomplishments, would begin lecturing at colleges across the country, demonstrating flights and investigating the physics behind flight. The flow of air over the wing would affect the next design of flying machines.
 In 1895, John J. Montgomery would own a patent for a better petroleum burning furnace. John Montgomery would be invited to take a teaching position with Santa Clara University in 1897. He would teach physics and other sciences. At the University in 1901, Montgomery would begin experimenting with Father Richard Bell on wireless telecommunications or radio, transmitting messages as far as San Francisco. In later years, he would demonstrate flight for hundreds of spectators at Santa Clara.
In 1895, John J. Montgomery would own a patent for a better petroleum burning furnace. John Montgomery would be invited to take a teaching position with Santa Clara University in 1897. He would teach physics and other sciences. At the University in 1901, Montgomery would begin experimenting with Father Richard Bell on wireless telecommunications or radio, transmitting messages as far as San Francisco. In later years, he would demonstrate flight for hundreds of spectators at Santa Clara.
 In 1903, John J. Montgomery would begin to develop this gliders again while teaching at Santa Clara University. He would also coin the word “aeroplane”, which later became “airplane”, and gain the patent in 1905 for the improvements of the technology. Inspired by the collaboration of a colleague, Montgomery would design a tandem winged glider with a propeller. The collaborator would take Montgomery’s propeller design and win first place at the World Fair in St. Louis, Missouri.
In 1903, John J. Montgomery would begin to develop this gliders again while teaching at Santa Clara University. He would also coin the word “aeroplane”, which later became “airplane”, and gain the patent in 1905 for the improvements of the technology. Inspired by the collaboration of a colleague, Montgomery would design a tandem winged glider with a propeller. The collaborator would take Montgomery’s propeller design and win first place at the World Fair in St. Louis, Missouri.
 Sometimes, competition is the healthiest thing for invention and innovation. John J. Montgomery wouldn’t be discouraged by the professional betrayal. Montgomery would lead several successful high elevation flights launched from balloons and maintaining flight for several minutes until gliding to a gradual stop. The Wright Brothers would also be taking flight around this time. What separated Montgomery’s work from other early aviators, besides beating them to flight by 20 years, was the duration of flight and the controlled figure eight patterns demonstrated. Montgomery’s machines wouldn’t have a motor at this point, but that wasn’t Montgomery’s priority. Safety and control were paramount to him.
Sometimes, competition is the healthiest thing for invention and innovation. John J. Montgomery wouldn’t be discouraged by the professional betrayal. Montgomery would lead several successful high elevation flights launched from balloons and maintaining flight for several minutes until gliding to a gradual stop. The Wright Brothers would also be taking flight around this time. What separated Montgomery’s work from other early aviators, besides beating them to flight by 20 years, was the duration of flight and the controlled figure eight patterns demonstrated. Montgomery’s machines wouldn’t have a motor at this point, but that wasn’t Montgomery’s priority. Safety and control were paramount to him.
 In July of 1905, Montgomery’s friend, colleague and test pilot, Daniel Maloney, would die testing on of his gliders on a balloon elevated flight. The Santa Clara, this version of the aeroplane, was flown hundreds times. The machine was damaged on a previous flight but hadn’t broken completely until that point. Maloney and Montgomery would’ve tested their gliders in the hills of Evergreen, as well as other places, before demonstrations in the City of San Jose and the University. This event and the big Earthquake of 1906 would cause Montgomery to take a little break from flying.
In July of 1905, Montgomery’s friend, colleague and test pilot, Daniel Maloney, would die testing on of his gliders on a balloon elevated flight. The Santa Clara, this version of the aeroplane, was flown hundreds times. The machine was damaged on a previous flight but hadn’t broken completely until that point. Maloney and Montgomery would’ve tested their gliders in the hills of Evergreen, as well as other places, before demonstrations in the City of San Jose and the University. This event and the big Earthquake of 1906 would cause Montgomery to take a little break from flying.
Montgomery would always be inventing and contributing to a wide range of industries. In 1909, perhaps inspired by hearing Nikola Tesla speak in 1893, John J. Montgomery would patent an alternating current rectifier. This would’ve improved radios and electrical vacuums at the time. The semi-conductor would replace this technology later on. Current Alternating Current Rectifiers are still used in DC (Direct Current) and high-voltage situations today. Most power sources around your house are grounded (GFC), not direct.
 Despite popular belief, John J. Montgomery didn’t actually live in the Village of Evergreen. Montgomery lived closer to Santa Clara University where he worked and the Pueblo of San Jose that built up around the Mission of Santa Clara. John Montgomery would come to get permissions from Evergreen’s Ramonda Family to fly on their ranch with the optimal hillsides to take flight from without the assistance of a balloon.
Despite popular belief, John J. Montgomery didn’t actually live in the Village of Evergreen. Montgomery lived closer to Santa Clara University where he worked and the Pueblo of San Jose that built up around the Mission of Santa Clara. John Montgomery would come to get permissions from Evergreen’s Ramonda Family to fly on their ranch with the optimal hillsides to take flight from without the assistance of a balloon.
John Montgomery would fly again in 1910, after finding his love. Montgomery fixed, immobilized, the tail of the airplane and incorporated the guiding features into the warping of the wing pattern. From there, John J. Montgomery was to add an engine and patent the design as the first plane. This design was titled “the Evergreen”.
 Unfortunately, during this series of flights and trials, John J. Montgomery would pass away after a landing he couldn’t walk away from. On October 31, 1911, Montgomery would fly through Evergreen for the last time. Without his contributions to the field and his competition that drove other inventors, we would be flying hundreds of miles an hour in metal tubes over a hundred years later. Beyond that, Montgomery was constantly improving upon technology and his work is around us everywhere, from our car tires to our electrical outlets.
Unfortunately, during this series of flights and trials, John J. Montgomery would pass away after a landing he couldn’t walk away from. On October 31, 1911, Montgomery would fly through Evergreen for the last time. Without his contributions to the field and his competition that drove other inventors, we would be flying hundreds of miles an hour in metal tubes over a hundred years later. Beyond that, Montgomery was constantly improving upon technology and his work is around us everywhere, from our car tires to our electrical outlets.
 The experiments and public demonstrations in Santa Clara County brought another claim to fame for the Valley of Heart’s Delight. If you didn’t know Evergreen’s famous fruit or famous wines, you would’ve heard about that guy who died flying there. The park and monument are here in Evergreen at Montgomery Hill Park along Yerba Buena Road and San Felipe Road, near where he passed. Another monument stands today at the Santa Clara University campus. Another airplane wing stands at the site of his San Diego County flights. You can also view his work at the Smithsonian Museum in Washington D.C or the much closer Hiller Museum in Redwood City. His great grandnephew has written a book and has agreed to our interview on the subject of John J. Montgomery and flight in general, at he follows in John’s footsteps as a professor of physics at UC Santa Cruz.
The experiments and public demonstrations in Santa Clara County brought another claim to fame for the Valley of Heart’s Delight. If you didn’t know Evergreen’s famous fruit or famous wines, you would’ve heard about that guy who died flying there. The park and monument are here in Evergreen at Montgomery Hill Park along Yerba Buena Road and San Felipe Road, near where he passed. Another monument stands today at the Santa Clara University campus. Another airplane wing stands at the site of his San Diego County flights. You can also view his work at the Smithsonian Museum in Washington D.C or the much closer Hiller Museum in Redwood City. His great grandnephew has written a book and has agreed to our interview on the subject of John J. Montgomery and flight in general, at he follows in John’s footsteps as a professor of physics at UC Santa Cruz.
 My experience and my knowledge of John J. Montgomery began with painting for the Evergreen School District at the school named in his honor. Otherwise, I would’ve remained unaware of the inventor. There, one of the ball walls specifically discusses the History of Aviation and where John J. Montgomery fits within that narrative. Gliders were incorporated into all the murals on campus.
My experience and my knowledge of John J. Montgomery began with painting for the Evergreen School District at the school named in his honor. Otherwise, I would’ve remained unaware of the inventor. There, one of the ball walls specifically discusses the History of Aviation and where John J. Montgomery fits within that narrative. Gliders were incorporated into all the murals on campus.
Other longtime Evergreen residents, like Jerry Kettmann, would’ve had an intimate relationship with aviation, cultivated at the nearby Hillview Airport. Harriet Quimby would’ve been directly inspired by Montgomery’s flights. Here’s the artwork we have planned for John J. Montgomery who helped put Evergreen on the map.

